Data security
We are currently using technology for everything. We store many essential/private things online, from personal photos to bank account details. We don’t want anyone to see our private data. We want all our information to be secure.
There are many ways in cryptography to secure data. In this blog, we aim to decode a few methods often used by developers, like encoding, masking, tokenization, encryption, and hashing.
Masking
Data masking is a method in which we try to hide sensitive data by replacing it with fake but similar data values like phone numbers (87****35) and email(x*****[email protected]).
You are trying to show the users bits of their data without revealing the actual values.
Data masking is an essential technique to ensure the privacy and security of sensitive data.
Tokenization
Tokenization is the method in which we generate a unique random token(string) and assign it to the data of the user that we want to store(Ex: Bank account number, phone number,…). We hold these user-token pairs in a token vault separate from your regular servers.
Data in the token vault is often encrypted. In the below example, it is stored as plain text.
 Reference: tokenization
Reference: tokenization
Encryption uses a mathematical method, while tokenization does not use any such thing. We will learn about encryption in the following sections.
Encoding
Encoding means changing one form of data to another.
Examples are converting string to JSON and JSON to string when data is being sent/received from the user.
From now on, we will discuss some commonly heard terms, hashing and encryption. I felt both serve the same purpose but later learned that’s not the case. Hashing and encryption are very similar, but they are not the same.
 seeing hashing and encryption
seeing hashing and encryption
We use encryption for transmitting data, whereas hashing is primarily used in securely storing passwords.
Hashing
In cryptography, a hash function is a mathematical algorithm that maps data of any size to a bit string of a fixed length.
Hashing is a one-way method for hiding sensitive data. The hashing algorithm transforms plaintext into a unique hash digest that requires significant effort to reverse the original plaintext.
One cannot revert something to its original form after it hashed. Even if we want to check if the inputted password is the same as yours, we hash the inputted password and check if both hashes match.
Some examples are SHA-1, SHA-2, MD5, CRC32, WHIRLPOOL, etc.
Encryption
A two-way function that takes in plaintext data and turns it into undecipherable ciphertext.
We use a public key to encrypt the data and a private key to decrypt the data. Only the user with a private key can revert it to its original form.
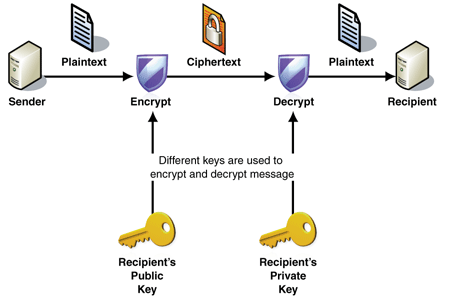 Reference: encryption
Reference: encryption
Encryption is commonly used in online banking, e-commerce, and secure messaging applications to protect sensitive information from being compromised during transmission.
Some examples are AES, RC4, DES, RSA, ECDSA, etc.
Frequently asked questions
How to decide whether to use encryption or tokenization?
People use tokenization when unsure if they can defend themselves against an attacker. Having no data is better than having data that you cannot secure. Tokenization is also centralizing the risk. You can go to a third party and request a token vault there. If this token vault breaches, the stakes are much higher, so you might have to consider those things when deciding.
Why is hashing not used in transmitting data?
We cannot use hashing on transmitted data because we must get the original data again after the transmission. Hence encryption is used.
Why is encryption not used for storing passwords?
-
People designed hashing algorithms specifically for storing passwords. They include various methods like salting and key stretching to make them resistant to attacks, making them more secure for password storage than general-purpose encryption algorithms.
-
If an attacker can get the decryption keys, they can extract all passwords in plain text without effort.
-
Hashing is faster than encryption. Hashing is necessary for every user login. Hence it is better to use something fast.
How to prevent attacks on hashing?
Always use slow hashes. Slow hashes take more time to hash a password, so attackers take more time to hash a given password; hence, they will get fewer hashed passwords in a given time.
More about hashing
SHA is suitable for hashing but unsuitable for password hashing as it is a fast hash.
Bcrypt uses a key stretching technique, where the hashing process happens many times to increase the time it takes to compute the final hash. We can adjust the number of times we perform the hashing process to fine-tune the time required for hash calculation and balance security and performance.
The purpose of the salt is to make it more difficult for an attacker to crack the password by using precomputed hashes (e.g., in a rainbow table). Using salt in password hashing helps to defend against dictionary attacks, where an attacker tries to crack a password by generating hashes for common words and comparing them to the stored hash.
Normal: Hash = hash_function(password) Salting: Hash = salt + hash_function(salt + password) Salted hash has a format like $x$y$z, x is the hash algorithm identifier(Ex: 2,2a,2b), and y is the cost/rounds. First, 22 letters of z consist of salt, and the remaining part contains the hashed password using that salt
Types of attacks on hashing
The rainbow table is an attack that contains all the precomputed hash values of some typical/famous passwords. It is not effective when salted hashes are used.
A dictionary attack is an attack that contains all the common/well-known passwords. A dictionary attack is only ineffective when people do not expect user passwords. When people use a random salt, a dictionary attack takes longer to crack the password.
Can we prevent attacks if we use many rounds in hashing?
The time to hash a password will exponentially increase if we increase the rounds.
Bcryptjs is used to get the below data.
Number of rounds => 5
Time taken => 14 ms
Password => qwerty123
Salt => $2a$05$wzcDCX6/PYgWBE/dLLOVn.
HashedPassword => $2a$05$wzcDCX6/PYgWBE/dLLOVn.EiqO5B.gNPEocIfGijaEXKwKdFyMVC.
Number of rounds => 10
Time taken => 79 ms
Password => qwerty123
Salt => $2a$10$oBUdFdQ3IWBFDG6Tz7yX8e
HashedPassword => $2a$10$oBUdFdQ3IWBFDG6Tz7yX8eQ7Lq9OolZsTNXVnmG/zQsoer7l7qEgC
Number of rounds => 20
Time taken => 65876 ms
Password => qwerty123
Salt => $2a$20$qZwROSSUbrnr6ribOz7YCe
HashedPassword => $2a$20$qZwROSSUbrnr6ribOz7YCeEyAK7NS.YrWYAFL/www8buIkQe3prNC
Number of rounds => 20
Time taken => 65876 ms
Password => qwerty123
Salt => $2a$20$qZwROSSUbrnr6ribOz7YCe
HashedPassword => $2a$20$qZwROSSUbrnr6ribOz7YCeEyAK7NS.YrWYAFL/www8buIkQe3prNC
With Bcrypt, we get several rounds for the hashing, so if I increase the number of rounds from 6 to 16, it is over 1,000 times more difficult to crack. If I increase it to 31, it is over 33 million times more difficult (2²⁵).
Conclusion
These are some of the methods used to keep data secure.
The increasing amount of data being generated and stored daily makes it more critical than ever to take the necessary steps to protect it. From implementing strong passwords and encryption to using data masking and access controls, there are many ways to safeguard your data from unauthorized access and theft.
Data security is everyone’s responsibility. Whether you’re an individual, a small business owner, or a large corporation, taking the necessary steps to protect your data and ensure its integrity is essential. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices in data security, you can help safeguard your information and ensure its safety for years.
